Google Updates Ping and Lastmod
June 27, 2023Hreflang X-Default – How to Use X-Default Effectively
September 13, 2023How to Measure Hreflang Success
The best way to measure the success of your Hreflang deployment is to evaluate it against the reason(s) you deployed it in the first place. The most common reason to deploy hreflang is to correct an incorrectly ranking market site from another market. For example, a search in Canada returns a US page rather than a Canada page. A byproduct of another market’s page ranking is traffic and sales cannibalization or a loss of sales due to cart abandonment.
Goal – Reduce SERP Cannibalization
Reducing SERP Cannibalization or getting more of a local market’s page ranking is often the most significant challenge and objective of using hreflang. Local market managers complain that when they or customers search for a product, they see a web page ranking from another market. While many SEOs are happy to have any page ranking, those with revenue goals need it to be the local market.
Success Metric – Management Happyness
In this case, the metric is a local manager being happy that their website is ranking rather than the incorrect market. Once Google processes the hreflang and swaps the market sites to the local market, the local manager is happy with the results, which is a win, and they stop complaining. That is a tricky metric to achieve as it requires them to do the queries and see that they are now the site ranking in the SERPS. Note, hreflang does NOT remove the other site from the SERPS; it only demotes it, so they may not be pleased.
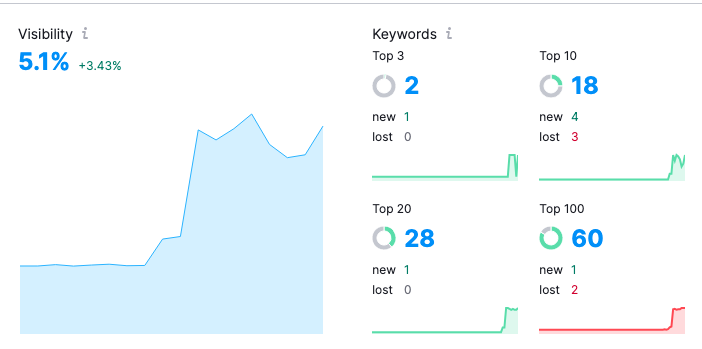
Success Metric – Increased Market Visibility
To achieve success, you use one of the SEO rank-checking tools to demonstrate an increase in the domain’s visibility in the market. Most SEOs use this goal to demonstrate that after deploying hreflang, more of the local market pages are ranking, resulting in increased visibility.
Goal – Increase Organic Search Traffic
It is logical that if the correct website ranks in the search results and people click, the local site will receive more organic traffic.
Success Metric – Organic Traffic Increased
Once the correct page is ranking in Google, you should see an increase in traffic to the market overall and, for those pages, being cannibalized. You can measure the increase with analytics or clicks to that page in Google Search Console. In many cases, the local market URL was not included in Google, so most of the organic traffic should be attributed to the Hreflang correction.
Goal – Increased Leads and Sales
The ultimate factor of performance is increased sales. Those markets that are cannibalized by another should realize an increase in traffic that can translate into leads and sales. It just makes sense that if the majority of their pages were excluded from the search index for being considered duplicates, they have a greater chance of generating traffic that will increase leads and sales when they appear and take their rightful position in the results.
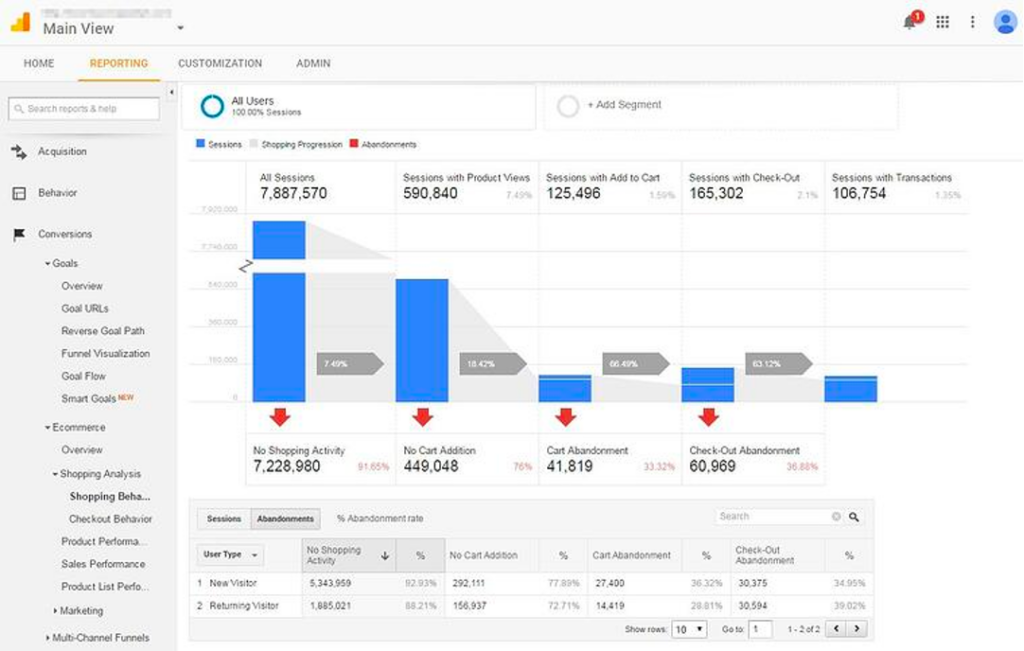
Success Metric – Reduced Cart Abandonment
Research reports have shown that as much as 88% of global shoppers abandon their shopping carts after adding items to them. The most common reasons are the lack of localization, non-local currency prices, shipping and return costs, and the challenging checkout process. Many of these issues are due to users landing on an incorrect market version of the website. The user is often unaware of these challenges until they get to the payment process.
Losing a potential customer at this point can be very costly. In our experience, a correctly implemented hreflang solution will direct searchers to the correct website. In your analytics, you should monitor the number of non-local prospects who abandon their cart. For example, if you manage the Australian sites and see that X% of non-Australian users abandon their carts, check to see if the Australian site ranks in those markets.
Success Metric – Increased Customer Satisfaction
The ultimate factor of client happiness and customer satisfaction is achieved when the hreflang deployment delivers searchers to the correct market engagement page, reducing the friction of purchasing from you. Many consumers get frustrated and feel betrayed by a brand with pricing different than expected due to being pushed to an incorrect market site.
Goal – Measure Hreflang Builder Success
Prospects often ask us how they can demonstrate the success of using Hreflang Builder. In several cases, we worked with them on a proof of concept where a set of pages is a subset of pages with a canonical or cannibalization problem selected and deployed in Hreflang Builder. We then will use one or more of the performance goals above to validate the benefit of using hreflang to solve the problem.
Any correctly implemented hreflang deployment can reduce cannibalization and increase visibility and traffic, which are great metrics for evaluating Hreflang Builder. Still, we suggest an additional set of operational metrics to measure the actual benefits of Hreflang Builder. Hreflang Builder has been developed to enable hreflang deployments for complex infrastructures, so how well it delivers on that goal should be measured.
Success Factor – Accelerate Hreflang Deployment
A critical success metric for Heflang Builder is how much faster were/are you able to deploy hreflang by using Hreflang Builder vs. internal coding, hacking a Python script, or copying and pasting a block of code in all the pages. In most cases, we can deploy at least a basic implementation of hreflang for an enterprise in 30 minutes or less if we are asked to “solve it” and don’t have to interact with others to deploy it. As long as we have a URL source, fundamental mapping rules, and a host, we can get a version typically with home pages, category pages, and “manager complaint” pages deployed the same day. The only delay is waiting on approvals and DevOps to upload the hreflang XML sitemaps.
Success Metric – Did it save you money?
Similar to the acceleration of deployment, saving money is another comparative factor relative to your challenge. If your CMS can manage hreflang correctly by clicking a button and deploying the code, that is the cheapest method. However, if your CMS cannot, or you have a complex infrastructure, you must either code a custom solution or use Hreflang Builder. On average, clients and prospects have told us they have received development estimates from $50,000 to $500,000 to implement a hreflang solution. Even for the most complex website that requires significant manual alternate mapping, the cost to deploy hreflang is significantly less with Hreflang Builder.
Success Metric – Percent of Mapped URLs
We have had a few clients that have used a percentage of mapped alternate URLs as their metric. This metric is included in the update confirmation.

Setting alternate URLs is one of the biggest challenges for companies. Using our 50+ alternate mapping rules, we can quickly identify alternates and create hreflang clusters. This metric informs the user of the number and overall percent of identified and mapped alternate URLs. The more mapped URLs mean less manual work for the client or agency and a more significant impact on cannibalization, demonstrating the solution’s value.
Success Metric – Level of Automation vs. Manual Effort
In most scenarios, we can completely automate the hreflang process with minimal human interaction. The percent automated KPI identifies the extent of automation and effort reduction for the client. For many users, they can achieve 100% automation. We can automatically import sources of URLs and apply mapping rules and output to an AWS bucket with a reverse proxy to their host. Those that don’t achieve 100% automation are caused by complex and diverse URL structures requiring manual intervention.
Hreflang Measurement FAQs
You will know your hreflang is working when Google provides the searcher with the appropriate language version or regional URL of content when they search for it. You can test this using a VPN, searching incognito in that market, or a rank-checking tool.